v Water Footprint
“The Water Footprint is an indicator of quantity of water consumed or polluted when producing a certain product, accounting for the water use throughout the entire production chain.”
A water footprint shows the extent of water use in relation to consumption by people. The water footprint of an individual, community or business is defined as the total volume of freshwater used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business.
The concept of water footprint was established in 2002 by Arjen Hoekstra as a consumption-based indicator of water use.
v Importance of water footprint
· Freshwater is a scarce resource; its annual availability is limited and demand is growing.
· The water footprint of humanity has exceeded sustainable levels at several places and is unequally distributed among people.
· And water shortage is becoming a greater concern to individuals, the environment and the economy.
v Types of water footprint
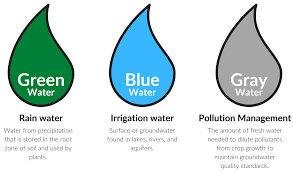
The water footprint has three components: Blue, Green and Grey.
1. Blue water footprint: refers to the amount of groundwater or surface water required to produce a product. Water is derived from sources such as aquifers, rivers or lakes. Domestic water use, industry and irrigated agriculture can each have a blue water footprint.
2. Green water footprint: refers to the amount of rainwater required to produce a product. It is mainly relevant for forestry, horticultural and agricultural products.
3. Grey water footprint: refers to the amount of freshwater required to assimilate pollutants in the production process to meet water quality standards. The grey water footprint considers point-source pollution discharged to a freshwater resource directly through a pipe or indirectly through runoff or leaching from the soil, impervious surfaces, or other diffuse sources.
v How to reduce Water Footprint??
In industries:
·Conserving water through measuring water consumption, installing water saving equipments, routine checks for pipes and training on awareness to employees etc.
·To install rain water harvesting system
·To increase recycling of water from process & utilities
·Achieving Zero liquid discharge (ZLD)
·Use of treated water from STP for greenbelt development and maintenance
At home:
·Fix any leaky taps
·Install water saving devices on sinks
·Fixing household leaks
·Using water-saving toilets
·Installing a water-saving shower head
·Only run off loads of laundry & dishes
In the garden:
·Install a water butt/large container for collecting rain that can be used for plants
·Use a watering can rather than a hose
·Water in the evening to reduce water loss
-By, Mrs. Priti S. Raval