Increasingly pressing problem worldwide: Water scarcity
Cause: Due to demographic growth, the
emigration of the population to large cities, ever-present effects of climate
change.
Ratio of water demand with the available supply is getting imbalances
and exceeding the present water supply already available.
To overcome this situation nowadays desalination, reuse & recycling
options are increasingly used to reduce the demand and supply gap in access
meeting the safe water criteria.
Seawater desalination has undergone significant developments in recent
years.
Humans cannot drink saline water but saline water can be made into
freshwater, for which there are many uses. The process is called
“desalination”, and it is being used more and more around the world
to provide people with needed freshwater.
Current scenario:
There are now about 21,000 desalination plants in operation around the
globe. The biggest ones are in the United Arab Emirates, Saudi
Arabia, and Israel.
The world’s largest desalination plant is located in Saudi
Arabia (Ras Al-Khair Power and Desalination Plant) with a capacity of
1,401,000 cubic meters per day.
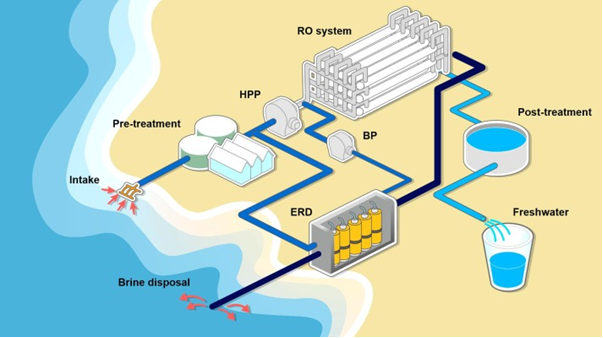
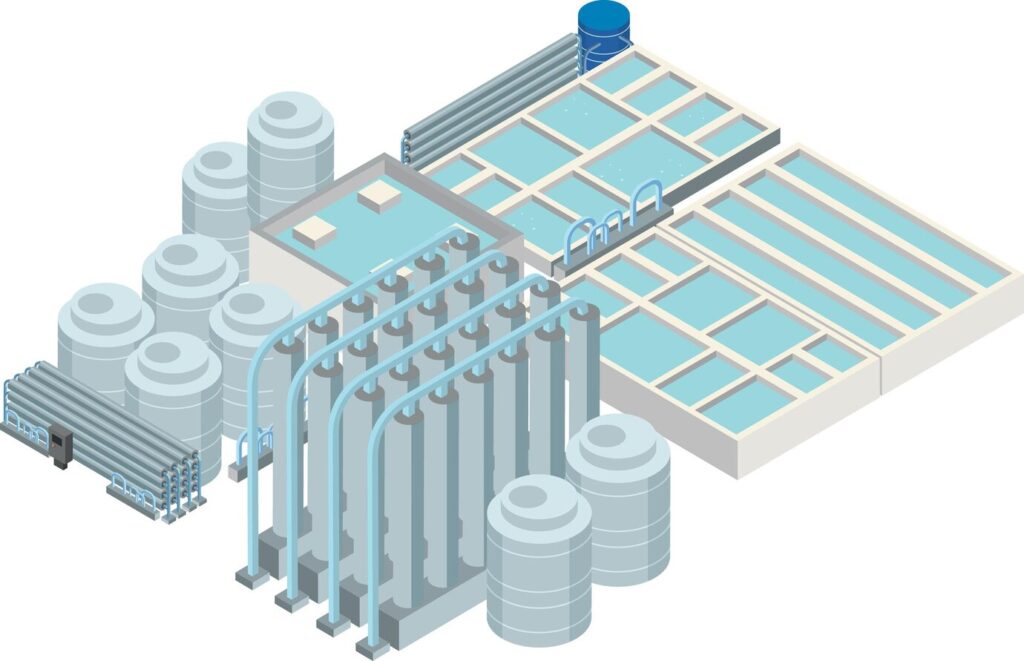
Image source: sciencedirect.com
Desalination processes used: (Source: www.iberdrola.com)
Ø Reverse Osmosis:
Most used process and consumes less energy than the rest, as it is based on the use of semipermeable membranes that allow the water to pass, but not the salt. These membranes are made of ultra-thin polyamide, which can become contaminated with bacteria so the water must be treated.
Ø Solar distillation:
Imitating the water cycle, it consists of evaporating seawater in large facilities with roofs where it is condensed and collected as fresh water. Although the energy used is the sun’s heat, large areas of land are required
Ø Electrodialysis:
It consists of moving the salt water through electrically charged membranes that trap the salt ions dissolved in the water, allowing fresh water to be extracted. There are diverse variants of electrodialysis, such as conventional and reverse
Ø Nanofiltration:
It is a process that uses nanotube membranes with higher permeability than reverse osmosis ones, which allows more water to be processed in less space using less energy. These membranes are manufactured with sulfonated compounds which, in addition to salt, eliminate traces of pollutants.
Ø Gas hydrate formation:
Gas hydrates are solid crystals that are formed by combining water with a gas, such as propane, at high pressure and at low temperature. During the process, all the salts and impurities present in the water disappear and as the temperature increases the gas can be recovered leaving fresh water
In addition, many desalination processes require heating water, pressurising it, or both, entailing a high energy cost. The solution in each case is to use renewable energy, such as solar, to reduce the consumption of the desalination plants.
Another possible sustainable desalination option is to use biotechnology, for example, by cultivating cyanobacteria that are capable of processing seawater, forming a low-salinity deposit around it.
-By,
Neha Jinit Bharambe
(Sr. Exe. Env.- Technical section)